

Messages (nerve impulses) from the brain travel along the spinal cord and control the activities of the body, such as the movement of the arms and legs, sensory functions like touch and temperature, and things we don't think about that go on in the background, like the function of the organs. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. The brain is connected to the rest of the body via the spinal cord and the nerves. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland control things like your body temperature, how fast you grow and tells you when you are thirsty. There are lots of interesting things that go on in the very middle of the brain, which is made of smaller parts known as the limbic system. CSF also helps to keep the brain healthy and working properly. The ventricles make the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that protect and cushion the brain and spinal cord. Hurting this part of the brain is very serious. In some ways this is the most important part of the brain because it keeps you alive. It sits at the top of the spine and receives messages from the rest of the body. The brain stem controls your lungs and heart and blood pressure. This allows you to stand up, walk in a straight line, and know if you are standing up or sitting down. The cerebellum sits at the back of the brain and controls your sense of balance. Your short term memory is also kept here.
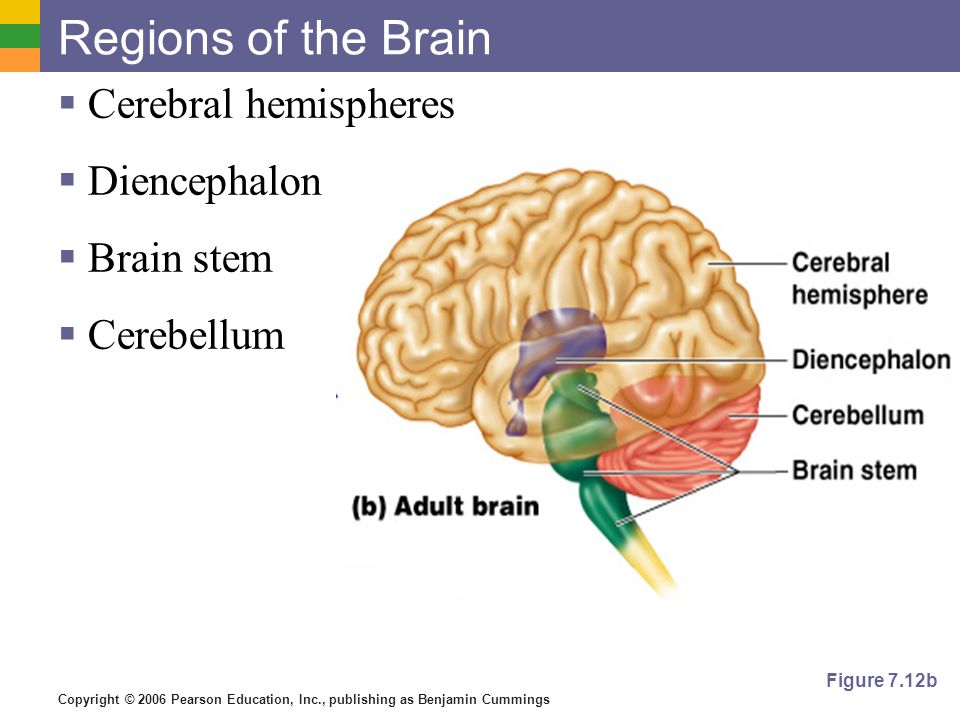
This part of the brain also recognises speech and is how you understand what someone says to you.
They receive messages from the ears so that you can recognise sound and messages. You have two temporal lobes, one behind each ear. This part of the brain tells you what is part of the body and what is part of the outside world. It figures out the messages you receive from the five senses of sight, touch, smell, hearing and taste. The parietal lobe gives you a sense of 'me'. This bit of the brain allows you to tell the difference between a square and a triangle. The occipital lobe receives messages from the eyes and recognises shapes, colours and objects. It is also where we solve problems and do most of our learning. This part of the brain allows us to speak. It is where we control our body movement and how we express ourselves. The frontal lobe governs our personality, character and behaviour. The main functions of CSF are to protect the brain (it acts as a shock absorber), to carry nutrients to the brain and remove waste from it. It is surrounded by a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The brain is very delicate and is well protected by the skull. Without the brain, the body would not be able to function. It controls everything that happens in the body, including vital functions like breathing and heartbeat. The brain is a complex organ that is enclosed inside the skull. Everything we do depends on the messages (nerve impulses) that are sent from the brain, along the spinal cord and on to the rest of the body. The brain and spine are vital to keep the body alive and functioning. Healthcare professionals Expand dropdown.Information and support Expand dropdown.Organise your own event Expand dropdown.Patient and carers' events Expand dropdown.Living with a neurological problem Expand dropdown.Seeking a diagnosis and care Expand dropdown.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
